Description: Summary of GV and CHPV
CHPV is promoted here as a more suitable alternative to some other voting systems under certain electoral conditions.
GV is primarily promoted as a useful analytical tool to evaluate CHPV and to compare it with other voting methods.
Properties and features of GV/CHPV that are highlighted in the preceding sections of this chapter are summarised below:

- Positional voting is a particular class of preferential voting.
- GV is in turn a particular class of positional voting.
- GV employs a sequence of rank-ordered positional weights that form a geometric progression.
- Analysis using GV can simultaneously handle an unlimited number of voters [V → ∞] and an unlimited number of candidates [N → ∞].
- The ratio of any two adjacent weights is called the common ratio of the geometric sequence.
- The common ratio has a fixed value between zero and one for any particular election. [0 ≤ r < 1]
- CHPV is GV with a common ratio of one half. [r = ½]
- The initial (first preference) weighting has no effect on the outcome of any GV/CHPV election and can be freely selected to simplify the count process. [a = any convenient scale factor]
- For CHPV only, each weighting is equal to the sum to infinity of all lower preference weightings.
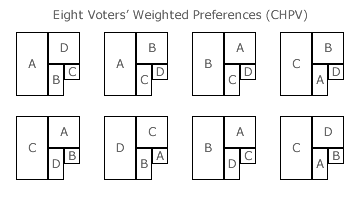
- For ranked ballot GV/CHPV, voting is by means of a suitable ballot where voters can express a uniquely ranked preference for each candidate.
- No gaps or duplications in the ranked sequence of expressed preferences are allowed.
- Voters may stop expressing (truncate) their preferences at any stage after indicating their first preference.
- For GV/CHPV, counting uses a simple, transparent and deterministic algorithm.
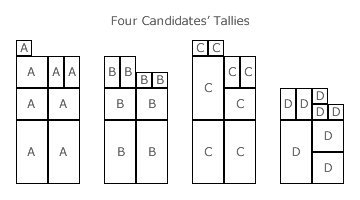
- The tally for each candidate is the sum of the weighted preference totals where each such total is the product of the total number of a given preference and its positional weighting.
- Tallies may be counted manually or electronically in GV elections using any integer, fractional, decimal number or binary number weightings provided 100% accuracy is maintained.
- When using CHPV, no rounding or approximation of tallies is ever required or permitted.
- The overall ranking of candidates from most to least preferred corresponds directly to the sequence of candidate tallies from highest to lowest respectively.
- The ranked ballot GV/CHPV algorithm is independent of the number of winners in an election.
- For a single-winner election, the most preferred (top-ranked) candidate wins.
- Where several winners are required, the two or more top-ranked candidates are elected to the two or more vacant seats respectively.
- Ties between two or more candidates with identical tallies where at least one is to be elected and at least one rejected are called critical ties.
- All other ties are non-critical ones.
- Critical ties must be resolved by random selection to determine the final outcome of an election.
- Party-list voting systems are used in multiple-winner multiple-party elections to ensure a reasonable degree of proportionality between vote share and seat share for each party.
- In closed party-list elections, each party issues its own rank-ordered list of its nominated candidates.
- For party-list CHPV, each successive candidate on a party list is awarded a consecutively halved fraction of the tally for their party.
- Irrespective of party affiliation, those candidates with the highest tallies (or 'averages') are declared the winners.
- Multiple-winner multiple-party CHPV is an example of a 'highest averages' party-list voting system.
- For free party-list elections, party-list CHPV can be used for the allocation of seats to parties while ranked ballot CHPV may be used by supporters of a party for the selection of its candidates to fill those allotted seats.
Proceed to next chapter > Evaluations (Ranked Ballot)
Skip to following chapter > Evaluations (Party-List)
Return to previous page > Description: Party-List
